How Augmented Reality for Healthcare Supports Doctors and Students
- David Bennett
- Nov 17, 2025
- 5 min read
Augmented Reality (AR) is rapidly becoming one of the most transformative tools in modern medicine. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in a fully digital world, AR overlays digital information onto the real environment—giving doctors and medical students real-time data, visuals, and guidance during critical tasks. This fusion of physical and digital environments elevates how clinicians learn, diagnose, plan surgeries, and treat patients.
From interactive anatomy overlays to AR-guided surgical navigation, AR offers a new dimension of clarity and accuracy that traditional training and clinical workflows cannot match. Innovators like Mimic Health XR, who are pioneering immersive healthcare technologies, are accelerating this shift by combining 3D visualization, mixed reality, and intelligent interactive training modules.
As AR continues to evolve—supported by more advanced hardware, 3D medical models, and AI integration—its value for doctors and students becomes increasingly indispensable. This article explores how augmented reality for healthcare is reshaping clinical training, supporting real-world medical procedures, and enhancing patient understanding.
What Is Augmented Reality in Healthcare?
Augmented Reality in healthcare blends digital information—like 3D anatomy, medical data, or guidance systems—directly into the clinician’s real-world view. Using AR smart glasses, mobile devices, or headsets, medical professionals can visualize crucial information right when they need it.
Core functionalities include:
Real-time overlays during surgical procedures
3D anatomy visualizations
Step-by-step procedural guidance
AR-enhanced medical simulations
Remote collaboration tools
Patient education models
AR bridges the critical gap between theoretical knowledge and hands-on application.
Why AR Matters for Doctors and Medical Students?
Doctors and students need clarity, precision, and practice in environments that are both high-pressure and high-consequence. AR supports them by transforming knowledge delivery and visual understanding.
AR enhances medical workflows by:
Reducing cognitive load
Enabling hands-free information access
Visualizing anatomy on real patients
Improving learning retention
Supporting diagnosis and real-time decision-making
The more complex the medical environment becomes, the more essential AR becomes in bridging knowledge and action.
AR for Medical Education & 3D Anatomy Learning
Traditional medical education relies heavily on textbooks, cadavers, and static images. AR brings anatomy to life with interactive 3D models that students can explore from any angle.
Benefits for medical students:
Real-time anatomical overlays during classes
Layered views of muscles, nerves, and organs
Interactive quizzes and task-based challenges
More engaging and memorable learning
Accessible learning anytime with mobile AR apps
Innovations in 3D medical training—like those explored in Mimic Health XR’s immersive education insights demonstrate how AR improves comprehension and retention dramatically.
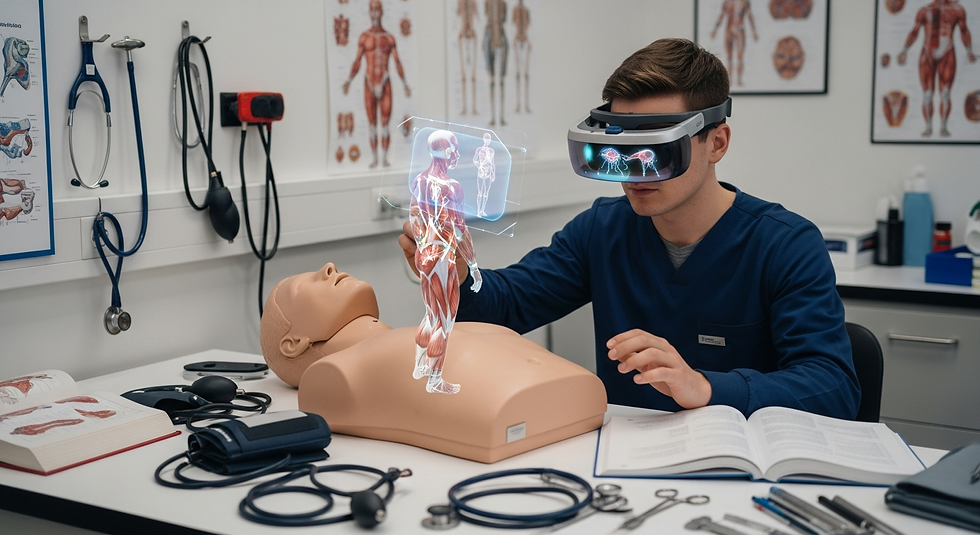
AR-Guided Surgical Planning & In-Procedure Assistance
AR is revolutionizing surgery by giving clinicians unprecedented visibility and accuracy during operations. Instead of relying solely on monitors, surgeons can visualize data directly over the patient.
AR supports surgeons by:
Displaying CT/MRI data over real anatomy
Highlighting incision points and risk areas
Providing 3D navigation for complex procedures
Offering step-by-step procedural guidance
Enabling team collaboration through shared visualizations
This leads to safer surgeries, fewer errors, and faster decision-making.

AR for Clinical Skill Development & Simulation
Simulation-based training is essential for developing confidence and competence. AR enables realistic practice without requiring expensive labs or physical models.
AR clinical training includes:
Hands-on procedural simulations
Stepwise AR overlays for learning techniques
Assessment modules that track accuracy
Team-based emergency response simulations
Realistic practice without patient risk
AR democratizes access to high-quality training, making it available anytime, anywhere.
AR for Rehabilitation & Therapy Support
AR provides dynamic, interactive tools for physical and cognitive therapy.
AR therapy benefits:
Guided physical therapy exercises
Real-time movement correction
Gamified rehab for motivation
Remote therapy modules
Cognitive support for stroke or brain injury patients
AR makes therapy engaging and measurable, improving outcomes and adherence.

AR for Patient Education & Engagement
Patients often struggle to understand medical procedures or diagnoses. AR turns complex information into easy-to-grasp visual experiences.
Patient-focused AR solutions:
3D explanations of medical conditions
Guided medication or device instructions
Clear visual storytelling for treatment plans
AR models during clinical consultations
These experiences reduce patient anxiety and improve informed decision-making.
AR in Remote Care & Teleconsultation
Augmented Reality expands telemedicine far beyond video calls, enabling interactive remote guidance.
AR transforms remote care by:
Allowing clinicians to annotate the patient’s real-world environment
Guiding patients through self-exams
Supporting remote specialist collaboration
Enabling AR overlays during teleconsultations
This leads to more accurate remote evaluations and better continuity of care.
Traditional Learning vs AR-Enhanced Learning
Feature | Traditional Healthcare Learning | AR-Enhanced Medical Learning |
Visualization | 2D diagrams, cadavers | Interactive 3D anatomy overlays |
Practice | Limited to labs/hospitals | Anywhere, anytime AR simulations |
Feedback | Manual, instructor-led | Instant digital assessment |
Engagement | Passive | Highly interactive |
Data Access | Separate screens/sources | Integrated into real-world view |
Cost | Requires physical resources | Scalable digital AR modules |
AR fills critical gaps in understanding, practice, and accessibility.
Industry Applications of AR in Healthcare
AR is now widely used across:
Medical schools & training centers
Surgical departments
Rehabilitation clinics
Emergency medicine
Mental health therapy
Radiology & imaging
Pharmaceutical visualization
Remote & rural healthcare
Its versatility makes it an essential tool for healthcare modernization.
Benefits of Augmented Reality for Healthcare
AR provides significant advantages for doctors & students:
Improved accuracy in treatments
Faster and more effective learning
Reduced surgical risk
Higher diagnostic clarity
Enhanced teamwork and communication
Better patient outcomes
Increased accessibility to advanced training
Higher retention through immersive education
AR is ultimately about improving competence, confidence, and care quality.
Challenges & Considerations
Despite rapid innovation, AR faces some limitations.
Main challenges:
High cost of advanced AR headsets
Training required for adoption
Limited integration with hospital systems
Data security concerns
Need for realistic haptic feedback
Regulatory approval for clinical use
As AR hardware becomes lighter, cheaper, and more connected to AI, many of these challenges will fade.
The Future of AR for Doctors and Students
The next decade will bring powerful advancements that blend AR, AI, and XR into fully adaptive medical ecosystems.
Future AR innovations include:
AI-enhanced AR tutoring systems
AR-driven personalized medical curricula
Real-time AR surgical coaching
Emotionally responsive AR therapy tools
Digital twins of organs & patients
Fully AR-supported operating rooms
Universal AR access through lightweight glasses
Holographic medical collaboration between cities or countries
This future mirrors the breakthroughs outlined in Advanced XR in Healthcare: A New Era, helping us imagine a world where AR becomes the standard framework for medical education and clinical excellence.
Conclusion
Augmented reality for healthcare is transforming how doctors operate, how students learn, and how patients understand their health. From immersive 3D anatomy models to surgical overlays and AR-based clinical simulations, the technology elevates accuracy, confidence, and efficiency across the entire medical ecosystem.
Organizations like Mimic Health XR—combining AR, VR, and 3D intelligence—are leading the evolution of immersive medical training and patient-centered care. As AR continues to evolve and integrate with AI and advanced 3D technology, it will become a cornerstone of medical education, diagnostics, and clinical innovation worldwide.
FAQs
1. How is augmented reality used in healthcare?
AR overlays digital information onto the real environment to support training, diagnosis, surgery, and patient education.
2. How does AR help medical students?
Students can explore 3D anatomy, practice procedures, and learn through interactive AR simulations that improve retention and understanding.
3. Can AR assist doctors during surgery?
Yes—AR can display imaging data over the patient, guide incisions, and offer real-time navigation support during complex surgeries.
4. Is AR useful for patient education?
Absolutely. AR helps patients visualize conditions, understand procedures, and follow treatment instructions more easily.
5. Does AR improve rehabilitation?
AR provides guided exercises, real-time feedback, and gamified therapy that increases patient motivation and recovery speed.
6. What equipment is needed for AR in healthcare?
AR can be delivered through smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, or advanced mixed reality headsets.
7. What is the future of AR in medicine?
Expect AI-enhanced surgical guidance, personalized medical training, digital twins, and fully AR-enabled clinical workflows.

.png)

Comments